What is shared writing?
Shared writing is a collaborative technique teachers use to help children develop ways to improve their writing. See an example of shared writing at work and an explanation of how it gives children a model of what they are expected to write.
What are time connectives?
Find out how your child's teacher will explain the concept of time connectives and ways in which your child will be encouraged to use them to improve their writing.
What are biography and autobiography?
In Key Stage 2 your child will learn about biographical and autobiographical texts. Find out about the features of these texts and help your child write their own texts at home.
What is an explanation text?
An explanation text is a specific type of writing and includes some identifiable features. Find out how your child's teacher will teach explanation texts and what your child needs to include in their own explanation texts.
What is a non-chronological report?
A non-chronological report is a piece of text that isn't written in time order. Find out how your child is taught to read and write non-chronological reports in primary school.
What is brainstorming?
Children learn how to brainstorm in school to generate ideas and solve problems. Find out how teachers encourage children to develop this skill and how it can help improve your child's written work.
What is a metaphor?
A metaphor is a figure of speech where two things that are normally unrelated are compared to each other. Find out how teachers explain metaphors to school children and how to encourage your child to spot metaphors and use them to improve their writing.
What is onomatopoeia?
Onomatopoeia is a word that names a sound, but also sounds like that sound. Find out how teachers explain onomatopoeia to school children and how to encourage your child to use it to improve their writing.
What is guided reading?
A guided reading or whole class reading session takes place every day in school. We explain what happens during these sessions and how you can help your child develop the skills of decoding and comprehension at home.
Teachers’ tips for reading comprehension
Reading comprehension exercises are a staple homework activity, not to mention a significant part of SATs. Lucy Dimbylow asked teachers for their insider tips on getting to grips with comprehension and how to help your child at home.
What is persuasive writing?
Persuasive text is written to make the reader do something. Children are taught this form of non-fiction text in Key Stage 2; we explain the key features of persuasive text and how you can support your child's learning at home.
What is a paragraph?
Paragraphs are sections of text, used to structure writing to make it clear and easy to read. We explain how the use of paragraphs is taught in KS2 and how you can help your child improve their writing by using paragraphs at home.
What is a story map or story mountain?
Your child will be taught to use different planning and analysis tools in primary literacy. Story maps, story flowcharts and story mountains are diagrams to help them think clearly about the plot and structure of what they're writing. We explain what parents need to know.
What are direct and indirect speech?
From Year 3 onwards your child will learn to write direct speech (quoting exact words spoken) and indirect speech (reporting a conversation). Our parents' guide covers the use of speech marks and how your child will cover this area of punctuation in the classroom.
What is a simile?
In Key Stage 2 children learn to recognise the use of figurative language in the texts they are reading. They will also be encouraged to use similes (and perhaps metaphors) in their writing. We explain how to identify similes and encourage your child to use them to improve their written work.
What is sentence level work?
Sentence level work is everything your child will be taught about grammar, text content and punctuation in the primary-school classroom. We offer some examples of activities to help them practise and improve their writing at home.
What is a suffix?
Suffixes are word endings. Children learn suffixes and how to use them to help them improve their spelling and understand of nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs. Find out more about how to help your child with KS1 and KS2 spelling and the use of suffixes in our guide.
What is a prefix?
Prefixes are groups of letters added to the beginning of a word, changing its meaning. Learning prefixes helps children with their spelling and vocabulary; we explain everything primary-school parents need to know about prefixes and spelling in KS1 and KS2.
What are simple, compound and complex sentences?
Simple sentences, compound sentences, complex sentences... can you identify the different types of sentence construction your child will learn in KS1 and KS2? Our parent-friendly guide sorts out any confusion and explains how your child will be taught to put grammar into practice in the classroom.
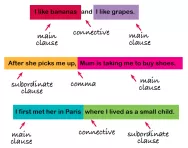
What is a clause?
From Year 1 onwards children are taught to write sentences made up of two clauses as part of sentence-level literacy work in the classroom. We explain everything you need to know about main and subordinate clauses in parent-friendly language.
What are prepositions?
Prepositions are some of the most common words in the English language. We explain how your child will learn to use them in primary school and why time connectives are so important in non-fiction writing.
What are connectives?
Has your child mentioned connectives? Connectives are joining words, and children will be taught to use them to connect phrases together into longer sentences and improve the flow of their writing. We explain what you need to know to help your child with sentence composition at home.
What is a homophone?
Homophones are tricky words which sound the same but have different meanings and are sometimes spelled differently (there, their and they're, for example). We explain how your child will be introduced to homophones in the classroom and tricks you can try at home to help them master homophone spelling.
What is personification?
In KS2 children often analyse figurative language when reading poetry and fiction. Personification, or giving a non-living object human characteristics to describe it, is a common technique children will study and learn to use in their own writing.
What is an adverb?
Adverbs give us more information about a verb, explaining how, when, where or why an action is taking place. We explain how children are taught to use adverbs to improve their writing in KS2, and how you can help at home.
What is an adjective?
Adjectives describe nouns, but how will your child be taught to use them correctly? We explain how word banks and a thesaurus can help improve your child's writing by encouraging them to use effective, powerful adjectives in their work.
Encourage a love of drama and the stage
Whether your child is a diva in the making or more inclined to be backstage crew, drama and acting could help develop skills that will offer a boost in many areas of life, says Lucy Dimbylow.
10 ways word puzzles can help your child
Crosswords, word searches and hangman aren’t just handy ways to keep your child quiet for five minutes; they could also boost their learning in some surprising ways. Here’s how…
Common handwriting problems and solutions
Illegible handwriting? Huge letters? Strange pencil grip? Struggles with left-handed writing? If your child is finding handwriting hard, perhaps it’s one of these four issues. Find out more about how to tackle these common problems with advice from the National Handwriting Association's Angela Webb.
What is a word bank?
Word banks are useful tools to help improve children's writing in KS1 and KS2. Find out how to create one at home and make expanding vocabulary a whole-family project!
What are powerful verbs?
Using powerful, descriptive verbs can make a big difference to your child's writing. We explain what parents need to know about powerful verbs (and ordinary verbs!) when helping with primary-school homework.
What is a play script?
Children learn to read, write and perform play scripts as part of the English and drama curriculum in primary school. Find out about the features of this genre, as well as ways to support your child's learning at home.
What are alliteration, assonance and consonance?
When analysing poetry your primary-school child might mention alliteration, assonance and consonance. We explain what they've been taught to look out for in literacy lessons.
What is an information text?
Information texts are an important part of primary school literacy lessons. We explain the features of this non-fiction genre, why note-taking matters and how to help your child at home.
What is a recount?
Has your child been asked to write a recount? Find out what the main features of this kind of non-fiction text are, plus how recounts are used in primary school literacy lessons.
What is argument text?
Argument texts are studied and written in KS2 literacy. We explain the features to look out for in this non-fiction genre and how to help your child structure and write their own argument text correctly.
What is instruction text?
We read instruction texts on an everyday basis. In primary school your child will be taught to recognise the main features and write increasingly complicated instruction texts as part of their non-fiction literacy work.
What is non-fiction?
Non-fiction texts are read, studied and written throughout the primary-school years. Our parents' guide covers instruction texts, recounts, information and explanation texts, persuasive writing and argument texts and explains what you need to know to support your child.
What are myths and legends?
Myths and legends are taught as part of the primary-school curriculum; as well as reading them your child will probably write their own version. We explain what parents need to know to support learning at home.
What is creative writing?
Children are encouraged to read and write a range of genres in their time at primary school. Each year they will focus on various narrative, non-fiction and poetry units; we explain how story-writing lessons help develop their story structure, grammar and punctuation skills.