Important update from TheSchoolRun
For the past 13 years, TheSchoolRun has been run by a small team of mums working from home, dedicated to providing quality educational resources to primary school parents. Unfortunately, rising supplier costs and falling revenue have made it impossible for us to continue operating, and we’ve had to make the difficult decision to close. The good news: We’ve arranged for another educational provider to take over many of our resources. These will be hosted on a new portal, where the content will be updated and expanded to support your child’s learning.
What this means for subscribers:
- Your subscription is still active, and for now, you can keep using the website as normal — just log in with your usual details to access all our articles and resources*.
- In a few months, all resources will move to the new portal. You’ll continue to have access there until your subscription ends. We’ll send you full details nearer the time.
- As a thank you for your support, we’ll also be sending you 16 primary school eBooks (worth £108.84) to download and keep.
A few changes to be aware of:
- The Learning Journey weekly email has ended, but your child’s plan will still be updated on your dashboard each Monday. Just log in to see the recommended worksheets.
- The 11+ weekly emails have now ended. We sent you all the remaining emails in the series at the end of March — please check your inbox (and spam folder) if you haven’t seen them. You can also follow the full programme here: 11+ Learning Journey.
If you have any questions, please contact us at [email protected]. Thank you for being part of our journey it’s been a privilege to support your family’s learning.
*If you need to reset your password, it will still work as usual. Please check your spam folder if the reset email doesn’t appear in your inbox.
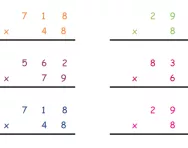
Multiplication problems using long multiplication
How do you do long multiplication in KS2?
Long multiplication, also known as column multiplication, is a method where numbers, typically a two- or three-digit number, are multiplied by another larger number in a written format.
Here's a simple overview of the steps for long multiplication:
- Write the numbers one on top of the other, aligning them on the right.
- Multiply each digit of the bottom number by each digit of the top number, starting from the right.
- Write the results below the line, shifting each result one place to the left for each digit in the bottom number.
- Add up all the numbers to get the final answer.
What is an example of long multiplication?
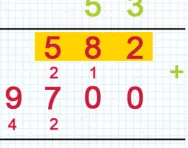
Here is a visual example of long multiplication:

You can see that we have multiplied each digit of the bottom number (22 by each digit of the top number (4234), starting from the right.
The smaller numbers underneath the final answer represent the tens digits that needed to be carried over to the next part of the sum. For instance, 6 + 8 = 14. The ten (1) was carried across and the unit (4) remains in the final answer.
What age do children learn long multiplication?
Typically introduced in Year 5 and Year 6, long multiplication becomes prominent once children are familiar with the grid method. The grid method aids in reinforcing the understanding of place value and the multiplication of multiples of ten and one hundred.
Once your child has grasped these concepts, long multiplication will be taught to them as a swifter and more efficient technique.
For more support with KS2 maths, check out our hub page, or try a new challenge such as this Long multiplication worksheet for Year 6.