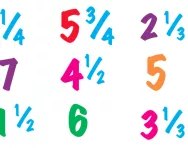What are number facts?
Children are expected to memorise a number of different number facts in primary school, including number bonds to 20 and the multiplication and division facts for the twelve times tables. We explain what number facts your child will be taught when and suggest easy ways to support their learning at home.
What is volume?
Volume and capacity are important concepts in primary maths, and your child will start learning about the amount of 3D space occupied by an object in Key Stage 1. Find out how you can support their learning at home, plus the relevant mathematical formulae, with our parents' guide to volume.
10 brilliant primary-school maths aids
Children often learn faster if they are allowed to use practical equipment to support them. Primary teacher Angela Smith explains what maths aids your child might find in the classroom, and how you can also use them at home to help your child practise important numeracy skills with hands-on, practical activities.
Why games-based learning is great for your child
If you despair of the amount of time your child spends attached to their tablet, think again: games and apps are an important part of their learning journey, from pre-school to secondary school, and can help to improve problem-solving skills and communication, as well as boost motivation. Lucy Dimbylow finds out why gaming means learning in the twenty-first century.
"He had problems counting up in twos, fives and even tens"
Lillian Blundell, from Bath, describes her experience of the SEN and school system with her son Robbie, 16, who has dyscalculia, and shares her tips for other parents.
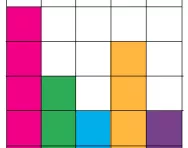
What is a block graph?
Block graphs are the first step in data handling and your KS1 child will learn to draw them, read them and use them to record information. We explain what you need to know about block diagrams and how they're used in the classroom.
10 ways playing cards helps children with maths
Fancy a quick game of cards? Studies show cognitive benefits to play and card games teach children new strategies for using mathematical information, categorising patterns, sequencing and sorting. Last but not least, this is numeracy practice the whole family will enjoy (though things might get a bit competitive... beware!). Kate Yelland asked maths teachers and experts why sitting down with a pack of cards and a primary-school child is definitely playing your cards right.
Primary numeracy glossary for parents
From area to word problems, TheSchoolRun's primary-school numeracy glossary offers a complete guide to all the maths concepts children are taught in EYFS, KS1 and KS2. Brush up on your own mathematical skills, clear up homework confusion and understand exactly what your child is learning at school by reading our basic definitions (with links to more detailed explanations, teachers' tips and examples).
What is a word problem?
We explain what a word problem is and give examples of the types of word problems your child might be challenged with in each primary-school maths year group, from Year 1 to Year 6.
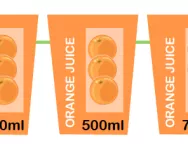
What is capacity?
We explain what capacity means and how children are taught to understand the concept in KS1 and learn about the relationship between millilitres and litres, and in KS2 use decimal notation to record the capacity of water and convert between units of measurement.
What are improper fractions and mixed numbers?
We explain what improper fractions and mixed numbers are and how the relationship between them can be taught to primary-school children.
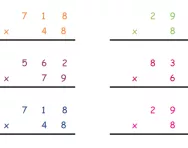
What is long multiplication?
We explain what the long multiplication method is and review how multiplication skills are built up through each year of primary school.
What are equivalent fractions and simplifying fractions?
We explain what equivalent fractions are, how the concept of equivalence is introduced in primary school maths and how knowledge of equivalent fractions is then used to simplify fractions.
What are multiples and factors?
We explain what multiples and factors are and how children are taught to recognise multiples from Year 1 and factors from Year 5, with examples of the types of problem they might be asked to solve.
What are standard and non-standard units?
We explain what standard and non-standard units are and how non-standard units can help children understand the concept of weight before they master the skill of accurate measurement and converting units of measurement
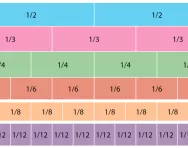
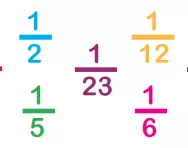
What are unit fractions?
We explain what unit fractions are and why children need to understand the concept of unit fractions before moving onto more advanced fractions learning.
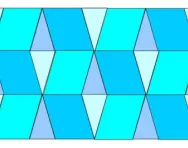
What are tessellating shapes?
We explain what tessellating shapes are and why tessellation may be taught in primary school as part of learning about 2D shapes.
What is an estimate?
We explain how children are taught to make estimates to check whether their answers are correct and how this skill is applied to more difficult calculations as your child advances through primary school.
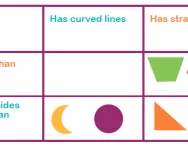
What is a Carroll diagram?
We explain what a Carroll diagram is and how primary-school children are taught to use a Carroll diagram to sort data, such as a group of objects or numbers, methodically.
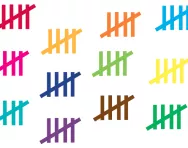
What is a tally chart?
We explain what a tally chart is and how children are taught to use a tally chart to collect data and interpret data on tally charts.
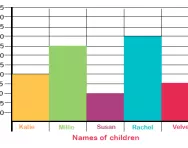
What is a bar chart?
We explain what a bar chart is and how children are taught to interpret a bar chart, produce their own bar charts on grid paper and on a computer, and produce bar charts with grouped discrete data.
100 of the best educational toys: stocking fillers
Don't forget the stockings! These little toys and games are the perfect size to slip in, yet still offer plenty of educational opportunity. Encourage observation, curiosity, dexterity and creativity with these brilliant gifts, whatever age your child is.
What is the bus stop method for division?
We explain what the bus stop method for division or short division is and why this is a quick and efficient method for working out division with larger numbers.
What is chunking?
We explain what chunking is and how this division technique is taught in primary school to help your child divide large numbers.
100 of the best educational toys: KS1
These games and toys consolidate early reading skills, help with simple maths calculations, boost strategic thinking and even introduce your KS1 child to engineering and geology! For literacy and numeracy fun in toy form, these are the games to try.
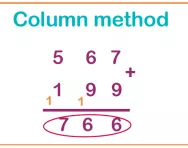
What is the column method?
We explain what the column method is, how it is set out and why it is an efficient method for working out addition and subtraction.
What are the four operations?
We explain what the four operations are and how children learn about addition, subtraction, multiplication and division over KS1 and KS2, working towards solving problems involving all four operations.
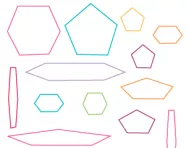
What are regular and irregular shapes?
We explain what regular and irregular shapes are and suggest mnemonics to help children remember how many sides different shapes have. We also have examples of the types of questions primary-school children might be asked about shapes.
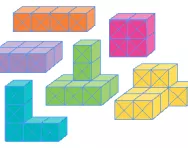
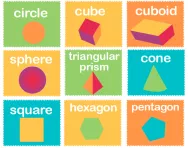
What are the properties of 2D and 3D shapes?
We explain what the properties of 2D and 3D shapes are, what faces, edges and vertices are and how children will describe 2D and 3D shapes in KS1 and KS2.
What are the names of 2D and 3D shapes?
We explain what the different 2D and 3D shapes are, when primary-school children are taught to name them and sort shapes according to their properties and when they learn to identify and draw their own nets of 3D shapes.
What is expanded notation?
We explain what expanded notation means, how it is taught in primary school and how it can help children with addition and multiplication calculations.
What are mathematical investigations?
We explain what types of mathematical investigations children will carry out in primary school and give examples of complex investigations they might be asked to solve in KS2.
What are analogue and digital?
We explain what analogue and digital are and how and when children are taught to read clock faces and convert between analogue and digital times in primary school.
What are time intervals?
We explain what time intervals are and how children are taught to work out time intervals in KS1 and KS2 maths.
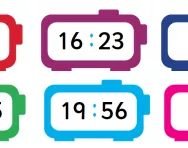
What are the 12-hour and 24-hour clock?
We explain how primary-school children are taught to use the 12-hour and 24-hour clock to tell the time on analogue and digital clocks, and how you can support their learning at home.
What are axes?
We explain what axes are and how your child will be taught to use axes on pictograms, bar charts and graphs.
What are arrays?
We explain what arrays are and give examples of how they can help children with their times tables learning and to explain the relationship between multiplication and division.
What is 'shared between'?
We explain what the term 'shared between' means and give examples of typical division problems your child might be set in KS1 and KS2.
What are clockwise and anti-clockwise?
We explain what clockwise and anti-clockwise means and give examples of typical exercises your primary-school child might be presented with to test their understanding of rotation.
What are equations?
We explain what equations are and how children are taught to solve equations in KS1 and KS2, as well as how the topic of algebra is introduced.